`
| |
|
Archive for the ‘Code Smells’ Category
Monday, October 28th, 2013
In the Agile India Submission system, we had a feature which would accept different url path to show matching proposals.
For example:
http://present.agileindia.org/agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle/45_mins –> will return all 45 mins proposals under the Agile-Lifecycle track for the Agile India 2014 Conference.
http://present.agileindia.org/agile-india-2014/beyond-agile/90_mins –> will return all 90 mins proposals under the Beyond-Agile track for the Agile India 2014 Conference.
If we remove the last part .i.e. http://present.agileindia.org/agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle –> will return all proposals under the Agile-Lifecycle track for the Agile India 2014 Conference.
and http://present.agileindia.org/agile-india-2014 –> will return all proposals for the Agile India 2014 Conference (could be other conferences as well.)
To achieve this, we had the following routes defined:
//URL Path = /agile-india-2014
app\get("/{conference}", function($req) {
$query_params = structure_request_params($req['matches']);
...
});
//URL Path = /agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle
app\get("/{conference}/{track}", function($req) {
$query_params = structure_request_params($req['matches']);
...
});
//URL Path = /agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle/45_mins
app\get("/{conference}/{track}/{label}", function($req) {
$query_params = structure_request_params($req['matches']);
...
}); |
//URL Path = /agile-india-2014
app\get("/{conference}", function($req) {
$query_params = structure_request_params($req['matches']);
...
});
//URL Path = /agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle
app\get("/{conference}/{track}", function($req) {
$query_params = structure_request_params($req['matches']);
...
});
//URL Path = /agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle/45_mins
app\get("/{conference}/{track}/{label}", function($req) {
$query_params = structure_request_params($req['matches']);
...
}); In our database we had the following:
CREATE TABLE `conference` (
`key` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
...
PRIMARY KEY (`key`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `track` (
`conference` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
`key` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
...
PRIMARY KEY (`key`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `label` (
`conference` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
`track` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
`key` VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
...
PRIMARY KEY (`conference`,`track`,`key`)
) ENGINE= InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `conference` VALUES ('agile-india-2014', ...);
INSERT INTO `track` VALUES ('agile-india-2014', 'agile-lifecycle', ...);
INSERT INTO `label` VALUES ('agile-india-2014', 'agile-lifecycle', '45_mins', ...); |
CREATE TABLE `conference` (
`key` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
...
PRIMARY KEY (`key`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `track` (
`conference` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`key` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
...
PRIMARY KEY (`key`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
CREATE TABLE `label` (
`conference` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`track` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`key` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
...
PRIMARY KEY (`conference`,`track`,`key`)
) ENGINE= InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `conference` VALUES ('agile-india-2014', ...);
INSERT INTO `track` VALUES ('agile-india-2014', 'agile-lifecycle', ...);
INSERT INTO `label` VALUES ('agile-india-2014', 'agile-lifecycle', '45_mins', ...); And some really complicated logic:
// For example URL Path /agile-india-2014 will result in
// $req_params = array('conference'=>'agile-india-2014')
// And URL Path /agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle will result in
// $req_params = array('conference'=>'agile-india-2014', 'track'=>'agile-lifecycle')
// And URL Path /agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle/45_mins will result in
// $req_params = array('conference'=>'agile-india-2014', 'track'=>'agile-lifecycle', 'label'=>'45_mins') |
// For example URL Path /agile-india-2014 will result in
// $req_params = array('conference'=>'agile-india-2014')
// And URL Path /agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle will result in
// $req_params = array('conference'=>'agile-india-2014', 'track'=>'agile-lifecycle')
// And URL Path /agile-india-2014/agile-lifecycle/45_mins will result in
// $req_params = array('conference'=>'agile-india-2014', 'track'=>'agile-lifecycle', 'label'=>'45_mins') function structure_request_params($req_params){
$query_params = array();
if(isset($req_params['label'])){
if(Conference::exists($req_params['conference'])){
$query_params['conference'] = $req_params['conference'];
if(Track::exists(array('conference' => $req_params['conference'], 'key' => $req_params['track']))){
$query_params['track'] = $req_params['track'];
if(Label::exists(array(
'conference' => $req_params['conference'],
'track' => $req_params['track'],
'key' => $req_params['label'])
)) {
$query_params['label'] = $req_params['label'];
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['label']);
}
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['track'], $req_params['label']);
}
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['conference'], $req_params['track'], $req_params['label']);
}
}
else{
if(isset($req_params['track'])){
if(Conference::exists($req_params['conference'])){
$query_params['conference'] = $req_params['conference'];
if(Track::exists(array('conference' => $req_params['conference'], 'key' => $req_params['track']))){
$query_params['track'] = $req_params['track'];
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['track']);
}
}
else{
if(Track::exists(array('key' => $req_params['conference']))){
$query_params['track'] = $req_params['conference'];
if(Label::exists(array('track' => $req_params['conference'], 'key' => $req_params['track']))){
$query_params['label'] = $req_params['track'];
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['track']);
}
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['conference'], $req_params['track']);
}
}
}
else{
if(isset($req_params['conference'])){
if(Conference::exists($req_params['conference'])){
$query_params['conference'] = $req_params['conference'];
}
elseif(Track::exists(array('key' => $req_params['conference']))){
$query_params['track'] = $req_params['conference'];
}
elseif(Label::exists(array('key' => $req_params['conference']))){
$query_params['label'] = $req_params['conference'];
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['conference']);
}
}
}
}
return $query_params;
} |
function structure_request_params($req_params){
$query_params = array();
if(isset($req_params['label'])){
if(Conference::exists($req_params['conference'])){
$query_params['conference'] = $req_params['conference'];
if(Track::exists(array('conference' => $req_params['conference'], 'key' => $req_params['track']))){
$query_params['track'] = $req_params['track'];
if(Label::exists(array(
'conference' => $req_params['conference'],
'track' => $req_params['track'],
'key' => $req_params['label'])
)) {
$query_params['label'] = $req_params['label'];
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['label']);
}
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['track'], $req_params['label']);
}
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['conference'], $req_params['track'], $req_params['label']);
}
}
else{
if(isset($req_params['track'])){
if(Conference::exists($req_params['conference'])){
$query_params['conference'] = $req_params['conference'];
if(Track::exists(array('conference' => $req_params['conference'], 'key' => $req_params['track']))){
$query_params['track'] = $req_params['track'];
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['track']);
}
}
else{
if(Track::exists(array('key' => $req_params['conference']))){
$query_params['track'] = $req_params['conference'];
if(Label::exists(array('track' => $req_params['conference'], 'key' => $req_params['track']))){
$query_params['label'] = $req_params['track'];
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['track']);
}
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['conference'], $req_params['track']);
}
}
}
else{
if(isset($req_params['conference'])){
if(Conference::exists($req_params['conference'])){
$query_params['conference'] = $req_params['conference'];
}
elseif(Track::exists(array('key' => $req_params['conference']))){
$query_params['track'] = $req_params['conference'];
}
elseif(Label::exists(array('key' => $req_params['conference']))){
$query_params['label'] = $req_params['conference'];
}
else{
$query_params['search_term'] = array($req_params['conference']);
}
}
}
}
return $query_params;
} And supporting model classes:
class Conference{
static function exists($conference){
DB::query('SELECT * FROM conference WHERE conference.key = %s', $conference);
return (DB::count() > 0);
}
}
class Track{
static function exists($query_params){
$search_query = Track::create_search_query($query_params);
DB::query("SELECT * FROM track WHERE $search_query");
return (DB::count() > 0);
}
private static function create_search_query($query_params){
$search_query = array();
foreach($query_params as $key => $value){
$search_query[] = "$key='$value'";
}
return join(' AND ', $search_query);
}
}
class Label{
static function exists($query_params){
$search_query = Label::create_search_query($query_params);
DB::query("SELECT * FROM label WHERE $search_query");
return (DB::count() > 0);
}
private static function create_search_query($query_params){
$search_query = array();
if(!empty($query_params)){
foreach($query_params as $key => $value){
$search_query[] = "$key='$value'";
}
return join(' AND ', $search_query);
}
return '';
}
} |
class Conference{
static function exists($conference){
DB::query('SELECT * FROM conference WHERE conference.key = %s', $conference);
return (DB::count() > 0);
}
}
class Track{
static function exists($query_params){
$search_query = Track::create_search_query($query_params);
DB::query("SELECT * FROM track WHERE $search_query");
return (DB::count() > 0);
}
private static function create_search_query($query_params){
$search_query = array();
foreach($query_params as $key => $value){
$search_query[] = "$key='$value'";
}
return join(' AND ', $search_query);
}
}
class Label{
static function exists($query_params){
$search_query = Label::create_search_query($query_params);
DB::query("SELECT * FROM label WHERE $search_query");
return (DB::count() > 0);
}
private static function create_search_query($query_params){
$search_query = array();
if(!empty($query_params)){
foreach($query_params as $key => $value){
$search_query[] = "$key='$value'";
}
return join(' AND ', $search_query);
}
return '';
}
} This was extremely hard to understand, so I decided to clean it up and get rid of the conditional complexity code smell.
Refactored code:
function structure_request_params($req_params){
$criteria = array('conference', 'track', 'label');
$params = array_values($req_params);
return build_search_query_params($criteria, $params, array());
}
function build_search_query_params($criteria, $params, $results) {
if(empty($params)) return $results;
if(empty($criteria)) {
if(!empty($params)) {
$results['search_term'] = $params;
}
return $results;
}
if(is_present_in_db($criteria[0], $params[0])) {
$results[$criteria[0]] = $params[0];
array_shift($params);
}
array_shift($criteria);
return map_criteria_params($criteria, $params, $results);
}
function is_present_in_db($table_name, $value){
return (DB::queryFirstField("SELECT count(*) FROM $table_name WHERE `key` = %s", $value) > 0);
} |
function structure_request_params($req_params){
$criteria = array('conference', 'track', 'label');
$params = array_values($req_params);
return build_search_query_params($criteria, $params, array());
}
function build_search_query_params($criteria, $params, $results) {
if(empty($params)) return $results;
if(empty($criteria)) {
if(!empty($params)) {
$results['search_term'] = $params;
}
return $results;
}
if(is_present_in_db($criteria[0], $params[0])) {
$results[$criteria[0]] = $params[0];
array_shift($params);
}
array_shift($criteria);
return map_criteria_params($criteria, $params, $results);
}
function is_present_in_db($table_name, $value){
return (DB::queryFirstField("SELECT count(*) FROM $table_name WHERE `key` = %s", $value) > 0);
} Also with this, we were able to delete the Model classes as they were not required.
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Design, Programming | No Comments »
Thursday, March 7th, 2013
Is writing inline comments always bad? Are comments really evil? I keep getting these questions over and over again.
Often you see code like this:
// If the item is taxable, get the taxed amount using tax calculator
if( objItem.bTaxable )
{
objItem.fTax = objCalculator.TaxForLocal(objItem.fItemRate);
}
// Additional tax is applicable if the item is an imported one
if( objItem.bImported )
{
objItem.fTax += objCalculator.TaxForImported(objItem.fItemRate);
}
// Add tax to item rate
objItem.fTaxedRate = objItem.fItemRate + objItem.fTax;
// Return the final amount
double fFinalAmount = objItem.fTaxedRate * objItem.nNumberOfItems;
return fFinalAmount; |
// If the item is taxable, get the taxed amount using tax calculator
if( objItem.bTaxable )
{
objItem.fTax = objCalculator.TaxForLocal(objItem.fItemRate);
}
// Additional tax is applicable if the item is an imported one
if( objItem.bImported )
{
objItem.fTax += objCalculator.TaxForImported(objItem.fItemRate);
}
// Add tax to item rate
objItem.fTaxedRate = objItem.fItemRate + objItem.fTax;
// Return the final amount
double fFinalAmount = objItem.fTaxedRate * objItem.nNumberOfItems;
return fFinalAmount; What is the real value of these comments?
When I see stuff like this, I usually tell people
When I was learning programming, I was thought that great programmers write great comments. These days I tell people lousy programmer write comments.
Immediately people who write inline-comments get defensive. And that’s completely understandably. I don’t think we’ve really explained our rationale for making such a ridiculous statement. So let me step back and explain the rationale.
Folks in the extreme-programming community will tell you:
Comments are often used as deodorant. Comments represent a failure to express an idea in the code. Try to make your code self-documenting or intention-revealing. When you feel like writing a comment, first try to refactor so that the comment becomes superfluous.

Most people will also tell you, that the biggest problem with comments is that they soon become outdated. The original intent of the person writing the comment was to help a developer who comes later to understand the code better. But unfortunately over a period of time, the comments get outdated and it adds more to the confusion. Speaking to many programmer, they simply delete or ignore the comments because they find them ambiguous. Even though the person who wrote the comments wrote them with a good intension, one needs to ask if it really solved any problem?
And then they question, why not put the same effort and time to write well-crafted code so that comments are never required? Is it impossible to do so?
While this argument is a good one, I find it hard to connivence people just based on this argument.
I’ve found the following approach work really well for me. First let’s understand why programmers write comments. Based on my experience, programmer write in-line comments for 3 different reasons:
- To explain what the code does
- To descrive how the code does what is does
- Why the code is written the way its written
If you think about it, the “what” and “how” of the code should really be expressed by self-documented code. IMHO its simply a failure on part of the programmer if they cannot express the “what” and “how” in the code itself.
However the “why” is little bit more tricky. It’s a reminder, telling us: “Hey, you are doing something complicated and someone else will not understand why. Even if you wrote a comment, they might not necessarily understand it.” At this point I might stop and see if there is a better way to design/model/code this, such that the why becomes obvious via the code. This is certainly more challenging and time consuming than to write a comment and moving on. However this short-term hack might bite me back. Luckily, most often than not, I can find a way to avoid the comment. But there are special cases when I need a comment to explain the why. Let’s see a few examples:
- There is a bug in the underlying framework/library I’m using. Searching on the net, I found the bug report and a workaround. Looking at just the code might not help someone understand the need for the workaround. Generally I would write a small comment saying Workaround with the version number of the framework/library and add the link to the workaround and continue. In future, someone can remove the workaround & delete the comment if the issue is fixed.
- I’m implementing a complex algo and its not common that everyone understands it. I would add a link to the Algo description (rather than duplicating the algo description in the code. DRY principle applies to comments as well.) and continue with my coding.
- And so on…
So think again before you leave a comment 😉
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Programming | No Comments »
Tuesday, October 9th, 2012
I’ve come to believe that Code is a liability. The less of it we have, the better off we are. Since code is a liability, would you not take extra care to keep it minimal and simple?
However I keep running into code shown below. I still wonder what drives developers to write more code, when they can do away with a fraction of it?
public class Calendar {
List<Integer> busySlots;
public void addBusySlot(int i) {
if(busySlots==null){
busySlots=new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
busySlots.add(i);
}
public boolean isFree(int time) {
if(busySlots==null)
return true;
return (!(busySlots.contains(time)));
}
} |
public class Calendar {
List<Integer> busySlots;
public void addBusySlot(int i) {
if(busySlots==null){
busySlots=new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
busySlots.add(i);
}
public boolean isFree(int time) {
if(busySlots==null)
return true;
return (!(busySlots.contains(time)));
}
} vs.
public class Calendar {
private final List<Integer> busySlots = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public void addBusySlot(int time) {
busySlots.add(time);
}
public boolean isFree(int time) {
return (!(busySlots.contains(time)));
}
} |
public class Calendar {
private final List<Integer> busySlots = new ArrayList<Integer>();
public void addBusySlot(int time) {
busySlots.add(time);
}
public boolean isFree(int time) {
return (!(busySlots.contains(time)));
}
} In fact I would argue that this is a Lazy Class and you can simply use the list directly where ever you need the Calendar.
Another example:
if(some_condition == true) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
} |
if(some_condition == true) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
} vs.
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Programming | 1 Comment »
Saturday, July 14th, 2012
Suppose we had the following (utterly) simplistic requirement:
@Test
public void politiciansDontNeedToPayTax() {
whenIncomeIs(10000).verify(POLITICIANS).pay(0);
}
@Test
public void residingAliensGetAwayByPayingLittleTax() {
whenIncomeIs(10000).verify(ALIENS).pay(1000);
}
@Test
public void richPeopleArePunishedWithHighestTax() {
whenIncomeIs(10000).verify(RICH_PEOPLE).pay(3000);
} |
@Test
public void politiciansDontNeedToPayTax() {
whenIncomeIs(10000).verify(POLITICIANS).pay(0);
}
@Test
public void residingAliensGetAwayByPayingLittleTax() {
whenIncomeIs(10000).verify(ALIENS).pay(1000);
}
@Test
public void richPeopleArePunishedWithHighestTax() {
whenIncomeIs(10000).verify(RICH_PEOPLE).pay(3000);
} where:
TaxPayer RICH_PEOPLE = new RichPeople();
TaxPayer ALIENS = new ResidingAliens();
TaxPayer POLITICIANS = new Politicians(); |
TaxPayer RICH_PEOPLE = new RichPeople();
TaxPayer ALIENS = new ResidingAliens();
TaxPayer POLITICIANS = new Politicians(); To fullfil this requirement, we’ve the following code:

Parent Class:
public abstract class TaxPayer {
protected abstract double getTaxPercentage();
public double calculateTaxAmount(final long income) {
if (getTaxPercentage() == 0)
return 0;
return income * getTaxPercentage() / 100.0;
}
} |
public abstract class TaxPayer {
protected abstract double getTaxPercentage();
public double calculateTaxAmount(final long income) {
if (getTaxPercentage() == 0)
return 0;
return income * getTaxPercentage() / 100.0;
}
} Each child class:
public class Politicians extends TaxPayer {
private double taxPercentage = 0;
@Override
protected double getTaxPercentage() {
return taxPercentage;
}
} |
public class Politicians extends TaxPayer {
private double taxPercentage = 0;
@Override
protected double getTaxPercentage() {
return taxPercentage;
}
} public class RichPeople extends TaxPayer {
private final double taxPercentage = 30;
@Override
protected double getTaxPercentage() {
return taxPercentage;
}
} |
public class RichPeople extends TaxPayer {
private final double taxPercentage = 30;
@Override
protected double getTaxPercentage() {
return taxPercentage;
}
} public class ResidingAliens extends TaxPayer {
private final double taxPercentage = 10;
@Override
protected double getTaxPercentage() {
return taxPercentage;
}
} |
public class ResidingAliens extends TaxPayer {
private final double taxPercentage = 10;
@Override
protected double getTaxPercentage() {
return taxPercentage;
}
} One would wonder what good are these child classes? Feels like a class explosion. Sure enough! This is the pathetic state of Object Oriented programming in many organizations, esp. the Enterprise software side of the world.
One could have easily used an enum to solve this problem:

public enum TaxPayer {
Politicians(0), Aliens(.1), RichPeople(.3);
private double taxPercentage;
private TaxPayer(double taxPercentage) {
this.taxPercentage = taxPercentage;
}
public double calculateTaxAmount(final long income) {
return income * taxPercentage;
}
} |
public enum TaxPayer {
Politicians(0), Aliens(.1), RichPeople(.3);
private double taxPercentage;
private TaxPayer(double taxPercentage) {
this.taxPercentage = taxPercentage;
}
public double calculateTaxAmount(final long income) {
return income * taxPercentage;
}
}
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Design, Programming, Training | 2 Comments »
Thursday, June 7th, 2012
Unfortunately many developers think they already know enough values and principles, so its not worth spending anytime learning or practicing them. Instead they want to learn the holy grail of software design – “the design patterns.”
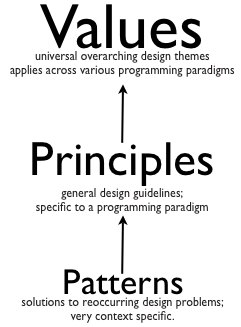
While the developers might think, design patterns is the ultimate nirvana of designing, I would say, they really need to learn how to think in their paradigm plus internalize the values and principles first. I would suggest developers should focus on the basics for at least 6 months before going near patterns. Else they would gain a very superficial knowledge about the patterns, and won’t be able to appreciate its true value or applicability.
Any time I get a request for teaching OO design patterns, I insist that we start the workshop with a recap of the values and principles. Time and again, I find developers in the class agreeing that they are having a hard time thinking in Objects. Most developers are still very much programming in the procedural way. Trying to retrofit objects, but not really thinking in-terms of objects and responsibilities.
Recently a student in my class shared that:
I thought we were doing Object Oriented Programming, but clearly its a paradigm shift that we still need to make.
On the first day, I start the class with simple labs, in the first 4-5 labs, you can see the developers struggle to come up with a simple object-oriented solution for basic design problems. They end up with a very procedural solution:
- main class with a bunch of static methods or
- data holder classes with public accessors and other or/er classes pulling that data to do some logic.
- very heavy use of if-else or switch
Its sad that teams don’t understand nor give importance to the following important OO concepts:
- Data and Logic together – Encapsulation (Everyone knows the definition of encapsulation, but how to put it in proper use, is always a big question mark.) Many developers write public Getters/Setters or Accessors by default on their classes. And are shocked to realize that it breaks encapsulation.
- Inheritance is the last option: It is quite common to see solutions where slight variation in data is modeled as a hierarchy of classes. The child classes have no behavior in them and often leads to a class explosion.
- Composition over Inheritance – In various labs, developers go down the route of using Inheritance to reuse behavior instead of thinking of a composition based design. Sadly, inheritance based solutions have various flaws that the team can’t realize, until highlighted. Coming up with a good inheritance based design, when the parent is mutable, it extremely tricky.
- Focus on smart data-structure: The developers have a tough time coming up with smart data-structure and putting logic around it. Via various labs, I try to demonstrate how designing smart data-structures can make their code extremely simple and minimalistic.
I’ve often noticed that, when you give developers a problem, they start off by drawing a flow chart, data-flow diagram or some other diagram which naturally lends them into a procedural design.
Thinking in terms of Objects requires thinking of objects and responsibilities, not so much in terms of flow. Its extremely important to understand the problem, distill it down to the crux by eliminating noise and then building a solution in an incremental fashion. Many developers have a misconception that a good designs has to be fully flushed out before you start. I’ve usually found that a good design emerges in an incremental fashion.
Even though many developers know the definition of high-cohesion, low-coupling and conceptual integrity, when asked to give a software or non-software example, they have a hard time. It goes to show that they don’t really understand the concept in action.
Developers might have read the bookish definition of the various Design Principles. But when asked to find out what design principles were violated in a sample design, they are not able to articulate. Also often you find a lot of misconception about the various principles. For example, Single Responsibility, few developers say that each method should do only one thing and a class should only have one responsibility. What does that actually mean? It turns out that SRP has to do more with temporal symmetry and change. Grouping behavior together from a change point of view.
Even though most developers raise their hands when asked if they know code smells, they have a tough time identifying them or avoiding them in their design. Developers need a lot of hands-on practice to recognize and avoid various code smells. Once you learn to recognize code smells, the next step is to learn how to effectively refactor away from them.
Often I find developers have the most expensive and jazzy tools & IDEs, but when you watch them code, they use their IDEs just as a text-editor. No automated refactoring. Most developers type “Public class xxx” instead of writing the caller code first and then using the IDE to generate the required skeleton code for them. Use of keyboard shortcuts is as rare as seeing solar eclipse. Pretty much most developers practice what I call mouse driven programming. In my experience, better use of IDE and Refactoring tools can give developers at least 5x productivity boost.
I hardly remember meeting a developer who said they don’t know how to unit test. Yet time and again, most developers in my class struggle to write good unit tests. Due to lack of familiarity or lack of practice or stupid misconceptions, most developers skip writing any automated unit tests. Instead they use Sysout/Console.out or other debugging mechanism to validate their logic. Getting better at their unit testing skills and then gradually TDD can really give them a productivity boost and improve their code quality.
I would be extremely happy if every development shop, invested 1 hour each week to organize a refactoring fest, design fest or a coding dojo for their developers to practice and hone their design skills. One can attend as many trainings as they want, but unless they deliberately practice and apply these techniques on job, it will not help.
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Design, Programming, Training | 1 Comment »
Thursday, June 7th, 2012
Following Object Oriented Design Principles have really helped me designing my code:
Along with these principles, I’ve also learned a lot from the 17 rules explained in the Art of Unix Programming book:
- Rule of Modularity: Write simple parts connected by clean interfaces
- Rule of Clarity: Clarity is better than cleverness.
- Rule of Composition: Design programs to be connected to other programs.
- Rule of Separation: Separate policy from mechanism; separate interfaces from engines
- Rule of Simplicity: Design for simplicity; add complexity only where you must
- Rule of Parsimony: Write a big program only when it is clear by demonstration that nothing else will do
- Rule of Transparency: Design for visibility to make inspection and debugging easier
- Rule of Robustness: Robustness is the child of transparency and simplicity
- Rule of Representation: Fold knowledge into data so program logic can be stupid and robust
- Rule of Least Surprise: In interface design, always do the least surprising thing
- Rule of Silence: When a program has nothing surprising to say, it should say nothing
- Rule of Repair: When you must fail, fail noisily and as soon as possible
- Rule of Economy: Programmer time is expensive; conserve it in preference to machine time
- Rule of Generation: Avoid hand-hacking; write programs to write programs when you can
- Rule of Optimization: Prototype before polishing. Get it working before you optimize it
- Rule of Diversity: Distrust all claims for “one true way”
- Rule of Extensibility: Design for the future, because it will be here sooner than you think
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Design, Programming | 1 Comment »
Saturday, August 6th, 2011
Consider the following code to retrieve a user’s profile:
public bool GetUserProfile(string userName, out Profile userProfile, out string msg)
{
msg = string.Empty;
userProfile = null;
if (some_validations_here))
{
msg = string.Format("Insufficient data to get Profile for username: {0}.", userName);
return false;
}
IList<User> users = // retrieve from database
if (users.Count() > 1)
{
msg = string.Format("Username {0} has {1} Profiles", userName, users.Count());
return false;
}
if (users.Count() == 0)
{
userProfile = Profiles.Guest;
}
else
{
userProfile = users.Get(0).Profile;
}
return true;
} |
public bool GetUserProfile(string userName, out Profile userProfile, out string msg)
{
msg = string.Empty;
userProfile = null;
if (some_validations_here))
{
msg = string.Format("Insufficient data to get Profile for username: {0}.", userName);
return false;
}
IList<User> users = // retrieve from database
if (users.Count() > 1)
{
msg = string.Format("Username {0} has {1} Profiles", userName, users.Count());
return false;
}
if (users.Count() == 0)
{
userProfile = Profiles.Guest;
}
else
{
userProfile = users.Get(0).Profile;
}
return true;
} Notice the bool return value and the use of out parameters. This code is heavily influenced by COM & C Programming. We don’t operate under the same constraints these days.
If we were to write a test for this method, what would it look like?
[TestClass]
public class ProfileControllerTest
{
private string msg;
private Profile userProfile;
//create a fakeDB
private ProfileController controller = new ProfileController(fakeDB);
private const string UserName = "Naresh.Jain";
[TestMethod]
public void ValidUserNameIsRequiredToGetProfile()
{
var emptyUserName = "";
Assert.IsFalse(controller.GetUserProfile(emptyUserName, out userProfile, out msg));
Assert.IsNull(userProfile);
Assert.AreEqual("Insufficient data to get Profile for username: " + UserName + ".", msg);
}
[TestMethod]
public void UsersCannotHaveMultipleProfiles()
{
//fake DB returns 2 records
Assert.IsFalse(controller.GetUserProfile(UserName, out userProfile, out msg));
Assert.IsNull(userProfile);
Assert.AreEqual("Username "+ UserName +" has 2 Profiles.", msg);
}
[TestMethod]
public void ProfileDefaultedToGuestWhenNoRecordsAreFound()
{
//fake DB does not return any records
Assert.IsTrue(controller.GetUserProfile(UserName, out userProfile, out msg));
Assert.AreEqual(Profiles.Guest, userProfile);
Assert.IsNull(msg);
}
[TestMethod]
public void MatchingProfileIsRetrievedForValidUserName()
{
//fake DB returns valid tester
Assert.IsTrue(controller.GetUserProfile(UserName, out userProfile, out msg));
Assert.AreEqual(Profiles.Tester, userProfile);
Assert.IsNull(msg);
}
} |
[TestClass]
public class ProfileControllerTest
{
private string msg;
private Profile userProfile;
//create a fakeDB
private ProfileController controller = new ProfileController(fakeDB);
private const string UserName = "Naresh.Jain";
[TestMethod]
public void ValidUserNameIsRequiredToGetProfile()
{
var emptyUserName = "";
Assert.IsFalse(controller.GetUserProfile(emptyUserName, out userProfile, out msg));
Assert.IsNull(userProfile);
Assert.AreEqual("Insufficient data to get Profile for username: " + UserName + ".", msg);
}
[TestMethod]
public void UsersCannotHaveMultipleProfiles()
{
//fake DB returns 2 records
Assert.IsFalse(controller.GetUserProfile(UserName, out userProfile, out msg));
Assert.IsNull(userProfile);
Assert.AreEqual("Username "+ UserName +" has 2 Profiles.", msg);
}
[TestMethod]
public void ProfileDefaultedToGuestWhenNoRecordsAreFound()
{
//fake DB does not return any records
Assert.IsTrue(controller.GetUserProfile(UserName, out userProfile, out msg));
Assert.AreEqual(Profiles.Guest, userProfile);
Assert.IsNull(msg);
}
[TestMethod]
public void MatchingProfileIsRetrievedForValidUserName()
{
//fake DB returns valid tester
Assert.IsTrue(controller.GetUserProfile(UserName, out userProfile, out msg));
Assert.AreEqual(Profiles.Tester, userProfile);
Assert.IsNull(msg);
}
} This code really stinks.
What problems do you see with this approach?
- Code like this lacks encapsulation. All the out parameters could be encapsulated into an object.
- Encourages duplication in both client code and inside this method.
- The caller of this method needs to check the return value first. If its false then they need to get the msg and do the needful. Its very easy to ignore the failure conditions. (In fact with this very code we saw that happen in 4 out of 6 places.)
- Tests have to validate multiple things to ensure the code is functions correctly.
- Overall more difficult to understand
We can refactor this code as follows:
public Profile GetUserProfile(string userName)
{
if (some_validations_here))
throw new Exception(string.Format("Insufficient data to get Profile for username: {0}.", userName));
IList<User> users = // retrieve from database
if (users.Count() > 1)
throw new Exception(string.Format(""Username {0} has {1} Profiles", userName, users.Count()));
if (users.Count() == 0) return Profiles.Guest;
return users.Get(0).Profile;
} |
public Profile GetUserProfile(string userName)
{
if (some_validations_here))
throw new Exception(string.Format("Insufficient data to get Profile for username: {0}.", userName));
IList<User> users = // retrieve from database
if (users.Count() > 1)
throw new Exception(string.Format(""Username {0} has {1} Profiles", userName, users.Count()));
if (users.Count() == 0) return Profiles.Guest;
return users.Get(0).Profile;
} and Test code as:
[TestClass]
public class ProfileControllerTest
{
//create a fakeDB
private ProfileController controller = new ProfileController(fakeDB);
private const string UserName = "Naresh.Jain";
[TestMethod]
[ExpectedException(typeof(Exception), "Insufficient data to get Profile for username: .")]
public void ValidUserNameIsRequiredToGetProfile()
{
var emptyUserName = "";
controller.GetUserProfile(emptyUserName);
}
[TestMethod]
[ExpectedException(typeof(Exception), "Username "+ UserName +" has 2 Profiles.")]
public void UsersCannotHaveMultipleProfiles()
{
//fake DB returns 2 records
controller.GetUserProfile(UserName);
}
[TestMethod]
public void ProfileDefaultedToGuestWhenNoRecordsAreFound()
{
//fake DB does not return any records
Assert.AreEqual(Profiles.Guest, controller.GetUserProfile(UserName));
}
[TestMethod]
public void MatchingProfileIsRetrievedForValidUserName()
{
//fake DB returns valid tester
Assert.AreEqual(Profiles.Tester, controller.GetUserProfile(UserName));
}
} |
[TestClass]
public class ProfileControllerTest
{
//create a fakeDB
private ProfileController controller = new ProfileController(fakeDB);
private const string UserName = "Naresh.Jain";
[TestMethod]
[ExpectedException(typeof(Exception), "Insufficient data to get Profile for username: .")]
public void ValidUserNameIsRequiredToGetProfile()
{
var emptyUserName = "";
controller.GetUserProfile(emptyUserName);
}
[TestMethod]
[ExpectedException(typeof(Exception), "Username "+ UserName +" has 2 Profiles.")]
public void UsersCannotHaveMultipleProfiles()
{
//fake DB returns 2 records
controller.GetUserProfile(UserName);
}
[TestMethod]
public void ProfileDefaultedToGuestWhenNoRecordsAreFound()
{
//fake DB does not return any records
Assert.AreEqual(Profiles.Guest, controller.GetUserProfile(UserName));
}
[TestMethod]
public void MatchingProfileIsRetrievedForValidUserName()
{
//fake DB returns valid tester
Assert.AreEqual(Profiles.Tester, controller.GetUserProfile(UserName));
}
} See how simple the client code (tests are also client code) can be.
My heart sinks when I see the following code:
public bool GetDataFromConfig(out double[] i, out double[] x, out double[] y, out double[] z)...
public bool AdjustDataBasedOnCorrelation(double correlation, out double[] i, out double[] x, out double[] y, out double[] z)...
public bool Add(double[][] factor, out double[] i, out double[] x, out double[] y, out double[] z)... |
public bool GetDataFromConfig(out double[] i, out double[] x, out double[] y, out double[] z)...
public bool AdjustDataBasedOnCorrelation(double correlation, out double[] i, out double[] x, out double[] y, out double[] z)...
public bool Add(double[][] factor, out double[] i, out double[] x, out double[] y, out double[] z)... I sincerely hope we can find a home (encapsulation) for all these orphans (i, x, y and z).
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Design, Programming | 1 Comment »
Thursday, July 21st, 2011
How would you kill this duplication in a strongly typed, static language like Java?
private int calculateAveragePreviousPercentageComplete() {
int result = 0;
for (StudentActivityByAlbum activity : activities)
result += activity.getPreviousPercentageCompleted();
return result / activities.size();
}
private int calculateAverageCurrentPercentageComplete() {
int result = 0;
for (StudentActivityByAlbum activity : activities)
result += activity.getPercentageCompleted();
return result / activities.size();
}
private int calculateAverageProgressPercentage() {
int result = 0;
for (StudentActivityByAlbum activity : activities)
result += activity.getProgressPercentage();
return result / activities.size();
} |
private int calculateAveragePreviousPercentageComplete() {
int result = 0;
for (StudentActivityByAlbum activity : activities)
result += activity.getPreviousPercentageCompleted();
return result / activities.size();
}
private int calculateAverageCurrentPercentageComplete() {
int result = 0;
for (StudentActivityByAlbum activity : activities)
result += activity.getPercentageCompleted();
return result / activities.size();
}
private int calculateAverageProgressPercentage() {
int result = 0;
for (StudentActivityByAlbum activity : activities)
result += activity.getProgressPercentage();
return result / activities.size();
} Here is my horrible solution:
private int calculateAveragePreviousPercentageComplete() {
return new Average(activities) {
public int value(StudentActivityByAlbum activity) {
return activity.getPreviousPercentageCompleted();
}
}.result;
}
private int calculateAverageCurrentPercentageComplete() {
return new Average(activities) {
public int value(StudentActivityByAlbum activity) {
return activity.getPercentageCompleted();
}
}.result;
}
private int calculateAverageProgressPercentage() {
return new Average(activities) {
public int value(StudentActivityByAlbum activity) {
return activity.getProgressPercentage();
}
}.result;
}
private static abstract class Average {
public int result;
public Average(List<StudentActivityByAlbum> activities) {
int total = 0;
for (StudentActivityByAlbum activity : activities)
total += value(activity);
result = total / activities.size();
}
protected abstract int value(StudentActivityByAlbum activity);
} |
private int calculateAveragePreviousPercentageComplete() {
return new Average(activities) {
public int value(StudentActivityByAlbum activity) {
return activity.getPreviousPercentageCompleted();
}
}.result;
}
private int calculateAverageCurrentPercentageComplete() {
return new Average(activities) {
public int value(StudentActivityByAlbum activity) {
return activity.getPercentageCompleted();
}
}.result;
}
private int calculateAverageProgressPercentage() {
return new Average(activities) {
public int value(StudentActivityByAlbum activity) {
return activity.getProgressPercentage();
}
}.result;
}
private static abstract class Average {
public int result;
public Average(List<StudentActivityByAlbum> activities) {
int total = 0;
for (StudentActivityByAlbum activity : activities)
total += value(activity);
result = total / activities.size();
}
protected abstract int value(StudentActivityByAlbum activity);
} if this were Ruby
@activities.inject(0.0){ |total, activity| total + activity.previous_percentage_completed? } / @activities.size
@activities.inject(0.0){ |total, activity| total + activity.percentage_completed? } / @activities.size
@activities.inject(0.0){ |total, activity| total + activity.progress_percentage? } / @activities.size |
@activities.inject(0.0){ |total, activity| total + activity.previous_percentage_completed? } / @activities.size
@activities.inject(0.0){ |total, activity| total + activity.percentage_completed? } / @activities.size
@activities.inject(0.0){ |total, activity| total + activity.progress_percentage? } / @activities.size or even something more kewler
average_of :previous_percentage_completed?
average_of :percentage_completed?
average_of :progress_percentage?
def average_of(message)
@activities.inject(0.0){ |total, activity| total + activity.send message } / @activities.size
end |
average_of :previous_percentage_completed?
average_of :percentage_completed?
average_of :progress_percentage?
def average_of(message)
@activities.inject(0.0){ |total, activity| total + activity.send message } / @activities.size
end
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Java, Programming, Programming Languages | 11 Comments »
Tuesday, July 5th, 2011
Single Dispatch: In most object-oriented programming languages, the concrete method that is invoked at runtime depends on the dynamic (runtime) type of the object on which the method is invoked.
For Example: If we have 2 cars; Car and derived class RubberCar.
public class Car
{
public virtual string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Wall";
}
}
public class RubberCar: Car
{
public override string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Wall";
}
} |
public class Car
{
public virtual string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Wall";
}
}
public class RubberCar: Car
{
public override string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Wall";
}
} and its test code
[Test]
public void SingleDispathWorksCorrectly()
{
Wall wall = new Wall();
Car currentCar = new Car();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Wall", currentCar.CrashInto(wall));
currentCar = new RubberCar();
Assert.AreEqual("Rubber Car crashed into the Wall", currentCar.CrashInto(wall));
} |
[Test]
public void SingleDispathWorksCorrectly()
{
Wall wall = new Wall();
Car currentCar = new Car();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Wall", currentCar.CrashInto(wall));
currentCar = new RubberCar();
Assert.AreEqual("Rubber Car crashed into the Wall", currentCar.CrashInto(wall));
} First time we call the method CrashInto() on currentCar, we are holding the reference of Car and hence Car’s CrashInto() method is invoked. However the second time, we’re holding the reference of RubberCar in currentCar and CrashInto() method from RubberCar is invoked correctly. In other words this is referred to as Polymorphism.
Its called Single Dispatch because one object’s runtime type (object on which the method is invoked) is used to decide which concrete method to invoke.
Double Dispatch: A mechanism that dispatches a method call to different concrete methods depending on the runtime types of two objects involved in the call (object and its parameter)
Let’s say, we had 2 types of wall, Wall and the derived class MagicWall.
Now when we called currentCar.CrashInto(new MagicWall()) we want to execute different behavior compared to currentCar.CrashInto(new Wall()). One classic way to implement this is:
// Car class
public virtual string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
if (wall is MagicWall)
return "Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
return "Car crashed into the Wall";
} |
// Car class
public virtual string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
if (wall is MagicWall)
return "Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
return "Car crashed into the Wall";
} // RubberCar class
public override string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
if (wall is MagicWall)
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Wall";
} |
// RubberCar class
public override string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
if (wall is MagicWall)
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Wall";
} This of-course works. However an alternative way to avoid the Switch Statement Smell and to truly use Double Dispatch is:
In Car:
public virtual string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Wall";
}
public virtual string CrashInto(MagicWall wall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
} |
public virtual string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Wall";
}
public virtual string CrashInto(MagicWall wall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
} and in RubberCar
public override string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Wall";
}
public override string CrashInto(MagicWall wall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
} |
public override string CrashInto(Wall wall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Wall";
}
public override string CrashInto(MagicWall wall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
} and its respective test:
[Test]
public void CarCanCrashIntoTheWall()
{
Wall wall = new Wall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Wall", new Car().CrashInto(wall));
}
[Test]
public void CarCanCrashIntoTheMagicWall()
{
MagicWall wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Magic Wall", new Car().CrashInto(wall));
} |
[Test]
public void CarCanCrashIntoTheWall()
{
Wall wall = new Wall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Wall", new Car().CrashInto(wall));
}
[Test]
public void CarCanCrashIntoTheMagicWall()
{
MagicWall wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Magic Wall", new Car().CrashInto(wall));
} and
[Test]
public void RubberCarCanCrashIntoTheWall()
{
Wall wall = new Wall();
Assert.AreEqual("Rubber Car crashed into the Wall", new RubberCar().CrashInto(wall));
}
[Test]
public void RubberCarCanCrashIntoTheMagicWall()
{
MagicWall wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("RubberCar crashed into the Magic Wall", new RubberCar().CrashInto(wall));
} |
[Test]
public void RubberCarCanCrashIntoTheWall()
{
Wall wall = new Wall();
Assert.AreEqual("Rubber Car crashed into the Wall", new RubberCar().CrashInto(wall));
}
[Test]
public void RubberCarCanCrashIntoTheMagicWall()
{
MagicWall wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("RubberCar crashed into the Magic Wall", new RubberCar().CrashInto(wall));
} Believe it or not, this is Double Dispatch in action. Which concrete method to invoke, depends on runtime type of 2 objects (car and wall.)
However there is a catch with this method. If you did the following:
[Test]
public void MethodOverloadingTakesPlaceAtCompileTime()
{
Wall wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Wall", new Car().CrashInto(wall));
// Instead of "Car Crashed into the Magic Wall"
} |
[Test]
public void MethodOverloadingTakesPlaceAtCompileTime()
{
Wall wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Wall", new Car().CrashInto(wall));
// Instead of "Car Crashed into the Magic Wall"
} Since MagicWall’s reference is held in wall, which is of type Wall at compile type and overloaded method are bound at compile time, this method behaves unexpectedly.
One way to fix this issue is to use vars in .Net.
[Test]
public void UseOfVarForcesMethodOverloadingToTakesPlaceAtRunTime()
{
var wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Magic Wall", new Car().CrashInto(wall));
} |
[Test]
public void UseOfVarForcesMethodOverloadingToTakesPlaceAtRunTime()
{
var wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Magic Wall", new Car().CrashInto(wall));
} In Languages that don’t support Double Dispatch, one needs to do the following:
[Test]
public void ToAvoidTheConfusion()
{
Wall wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Magic Wall", wall.CollidesWith(car));
Assert.AreEqual(0, car.DentCount);
}
[Test]
public void DoubleDispatch_OnWall()
{
Wall wall = new Wall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Wall", wall.CollidesWith(car));
Assert.AreEqual(1, car.DentCount);
} |
[Test]
public void ToAvoidTheConfusion()
{
Wall wall = new MagicWall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Magic Wall", wall.CollidesWith(car));
Assert.AreEqual(0, car.DentCount);
}
[Test]
public void DoubleDispatch_OnWall()
{
Wall wall = new Wall();
Assert.AreEqual("Car crashed into the Wall", wall.CollidesWith(car));
Assert.AreEqual(1, car.DentCount);
} Production Code:
public class Wall
{
public virtual string CollidesWithCar(Car car)
{
return car.CrashIntoWall(this);
}
public virtual string CollidesWithRubberCar(RubberCar car)
{
return car.CrashIntoWall(this);
}
}
public class MagicWall : Wall
{
public override string CollidesWithCar(Car car)
{
return car.CrashIntoMagicWall(this);
}
public override string CollidesWithRubberCar(RubberCar car)
{
return car.CrashIntoMagicWall(this);
}
} |
public class Wall
{
public virtual string CollidesWithCar(Car car)
{
return car.CrashIntoWall(this);
}
public virtual string CollidesWithRubberCar(RubberCar car)
{
return car.CrashIntoWall(this);
}
}
public class MagicWall : Wall
{
public override string CollidesWithCar(Car car)
{
return car.CrashIntoMagicWall(this);
}
public override string CollidesWithRubberCar(RubberCar car)
{
return car.CrashIntoMagicWall(this);
}
} public class Car
{
public virtual string CrashIntoWall(Wall wall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Wall";
}
public virtual string CrashIntoMagicWall(Wall magicWall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
}
}
public class RubberCar:Car
{
public override string CrashIntoWall(Wall wall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Wall";
}
public override string CrashIntoMagicWall(Wall magicWall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
}
} |
public class Car
{
public virtual string CrashIntoWall(Wall wall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Wall";
}
public virtual string CrashIntoMagicWall(Wall magicWall)
{
return "Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
}
}
public class RubberCar:Car
{
public override string CrashIntoWall(Wall wall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Wall";
}
public override string CrashIntoMagicWall(Wall magicWall)
{
return "Rubber Car crashed into the Magic Wall";
}
} We can expand the same technique to use more than 2 objects to decide which concrete method to invoke at run time. This mechanism is called Multiple Dispatch.
Posted in Code Smells, Design, Programming | 2 Comments »
Sunday, May 15th, 2011
Many people will argue that there is more badly written code than good code. And its important to write comments to avoid these situations. Therefore we should encourage (force) people to write comments.
IMHO they are absolutely right that today many project suffer from poorly written code without any (good) comments. However every team I know, that suffers from this problem, has always been told (forced) to write comments. In spite of the emphasis on writing comments it has not really helped them.
I usually ask:
By asking developers to write comments are we really addressing the root of the problem?
.i.e. developers don’t invest quality time to write self-documenting code; code that clearly communicates its intent and does not require the deodorant of comments.
May be its time to try something different?
I have seen this myself many times, when we emphasize & educate the team on how to write clean code and ask them to stop wasting time writing comments, the code starts to communicate lot better. Its lot more maintainable. Also we have found that writing automated tests is a great way to document your intent as well.
This is how I would explain the concept Comments Smell to a team:
Writing comments that explain “how” or “what” the code does, what it does, is evil IMHO. Comments (esp. about what and how) is a clear failure to express the intent in code. Comment is a deodorant to hide that failure (smell).
- If developers don’t invest time to write clear code, what is the guarantee that they will write clear comments?
- Is doing a mediocre job at both (comments and code) better than doing a great job at just Code?
- Will it actually be more productive to do both or just one?
Remember the biggest problem with comments it that they fall out-of-sync with code very soon. So its not just about the extra investment to write good comments, but also the investment to maintain them.
One has to think hard to write code that expresses intent rather than write some sloppy code with poor abstractions and get away (washing their hands off) by writing comments. Developers have to take responsibility for writing code that others can easily understand.
Having said that, there are times when “the why” (why we are doing something in the code, a particular way) is not apparent by just looking at the code. So if we don’t find a suitable way to communicate “the why” through code, comment is the fall back option.
Note that comments are a fall back option in “the why” case rather than a default option.
Posted in Agile, Code Smells, Programming, Training | 3 Comments »
|






